Which Best Describes an Example of an N-type Semiconductor
Phosphorous P in silicon. N-type Semiconductor Example An intrinsic semiconductor material like Silicon Si has 14 electrons with a configuration of 284 and Germanium Ge has 32 electrons with a configuration of 28184.
What Are Intrinsic Semiconductors Explain How A Semiconductor Can Be Converted Into An N Type Semiconductor Quora
Example of trivalent inpurities are aluminium or boron.
. Examples of pentavalent impurities are Arsenic Antimony Bismuth etc. The electron acceptor is responsible for the formation of a hole by accepting an electron from the lattice. If the intrinsic semiconductor is doped with an electron acceptor in order to make it as a p-type semiconductor.
Example of pentavalent impuritie are phosphorus or arsenic. N-type and p-typeA p-type semiconductor is one in which the impurity added produces extra holes available for. Which best describes an example of a p-type semiconductor.
It uses gallium so. As a result majority carriers in the p-type semiconductor formed are holes. The pentavalent impurities provide extra electrons and are termed as donor atoms.
Hence it is called n-type semiconductor. The majority carriers in a p-type semiconductor are holes. Which of the following statements best describes semiconductors.
Electrons are the majority charge carriers in n-type. Which best describes an example of an n-type semiconductor. As conduction is due to a large number of free electrons the electrons in the n-type semiconductor are the MAJORITY CARRIERS and holes are the MINORITY CARRIERS.
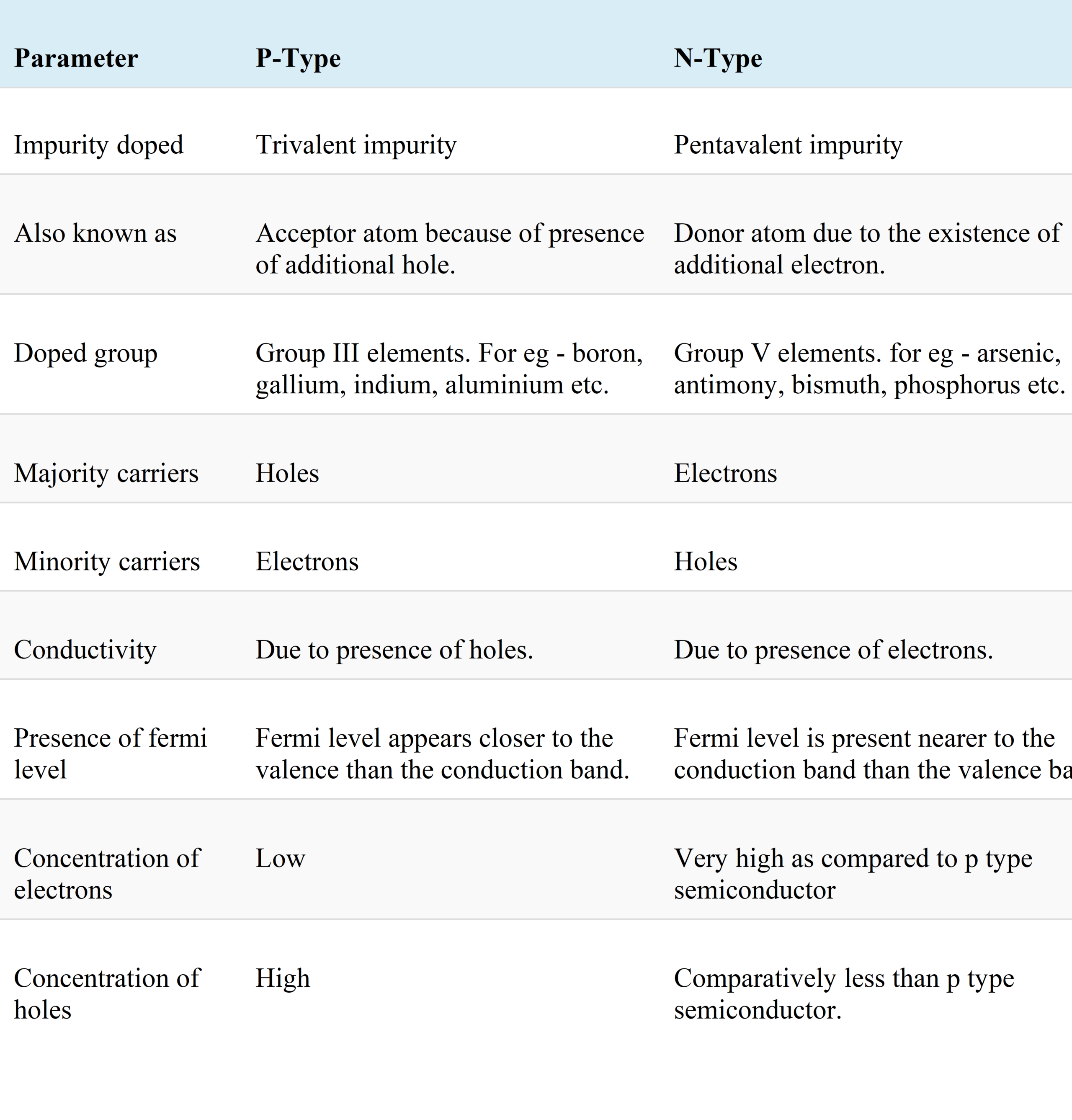
In an n-type semiconductor pentavalent impurity from the V group is added to the pure semiconductor. All of the above use low power fast switching reliable economic. D It uses boron so that electrical conduction is due to the movement of electrons.
It has holes in majority and electrons in minority. Which best describes an example of a p-type semiconductor. Mainly due to holes.
ExplanationA semiconductor is a substance whose resistivity is between that of a good conductor and a good insulatorThere are two types of semiconductor. Each atom requires 8 electrons in its valence shell to be stable. What is n-type and p-type semiconductor with example.
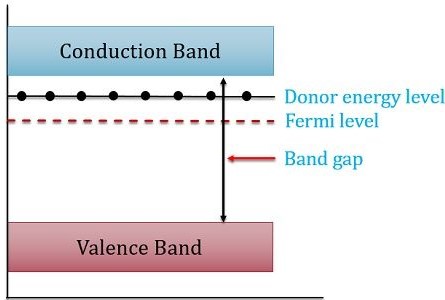
Why are semiconductors valuable in modern electronics. P-type - When we use trivalent impurities for doping then we get a p-type semiconductor. What is a P-Type Semiconductor.
The conduction electrons are completely dominated. The low lands i believe. For example a silicon crystal doped with boron group III creates a p-type semiconductor whereas a crystal doped with phosphorus group V results in an n-type semiconductor.
Gallium or Boron is a common p-type dopant for siliconIt has large numbers of holes provided by the trivalent atoms which are electrically neutral and. Crystal as a whole is neutral but the donor atom becomes an immobile positive ion. A P-type semiconductor uses boron so that electrical conduction is due to the movement of electrons.
A p-type semiconductor is formed by doping an intrinsic semiconductor with trivalent impurity for example Boron Aluminium Indium Gallium etc. Answer Dit uses boron so that electrical conduction is due to the movement of positive charge. Silicon having 4 electrons in its outer shell while phosphorous has 5 electrons.
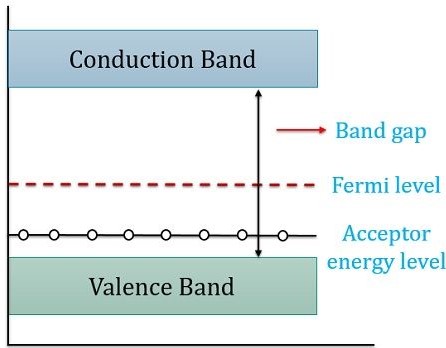
What is an n-type Semiconductor. An n-type semiconductor is made by adding a small amount of a Group-V element such as phosphorous P or arsenic As to the intrinsic semiconductorGroup-V elements have five valence electrons per atom. N- type - When we use a pentavalent impurity for doping then we get a n-type semiconductor.
Which of the following is true about this band diagram. Therefore when theses atoms make bonds with the Group-IV atoms due to the atomic structure of the material only. It uses gallium so that electrical conduction is due to the movement of electrons.
An n-type semiconductor is one in which the impurity added produces more extra electrons available for conduction eg. 0 It uses phosphorus so that electrical conduction is due to the movement of electrons. Density of states a.
It uses phosphorus so that electrical conduction is due to the movement of a positive charge. So a spare electron is produced.
![]()
Electronics The Science Of Electronics Britannica
Differences Between P Type And N Type Semiconductor Linquip
![]()
Band Diagram For Activation Energy In N Type Semiconductor Download Scientific Diagram

Pn Junction Theory For Semiconductor Diodes
![]()
1 Properties Of Semiconductors Hitachi High Tech Global

Simple Basic Led Circuit Circuit Diagram Led Projects Circuit Diagram Electronics Projects Diy
![]()
I P Type N Type Semiconductors Engineering Libretexts
![]()
A The Structure Model Of The N Type Semiconductor Electrolyte Download Scientific Diagram
In N Type Semiconductors Does The Free Electron Or Extra Electron From The Pentavalent Donor Not Contribute In The Formation Of A Hole Quora
Differences Between P Type And N Type Semiconductor Linquip
![]()
Differences Between P Type And N Type Semiconductor Linquip
![]()
Band Diagram For Activation Energy In P Type Semiconductor Download Scientific Diagram
Differences Between P Type And N Type Semiconductor Linquip
Differences Between P Type And N Type Semiconductor Linquip

Lesson Explainer Doped Semiconductors Nagwa
![]()
Mechanism Of Photoelectrocatalysis And The Main Reactions For A N Type Download Scientific Diagram
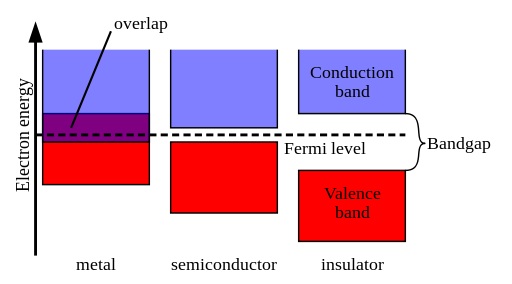
Differences Between P Type And N Type Semiconductor Linquip
A The Structure Model Of The N Type Semiconductor Electrolyte Download Scientific Diagram
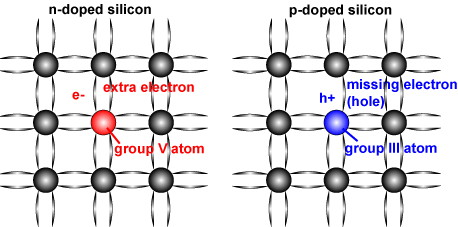
Comments
Post a Comment